Why Your Anxiety Creates Real Physical Pain

Why Your Anxiety Creates Real Physical Pain: The Hidden Inflammation Connection
The science behind why worry makes your body hurt—and what to do about it
If you've ever felt like your anxiety is attacking your body with chest tightness, stomach knots, muscle aches, or feeling “sick,” you’re experiencing something measurable. These symptoms are not “just in your head”—they reflect biological stress-inflammation pathways that can be addressed.
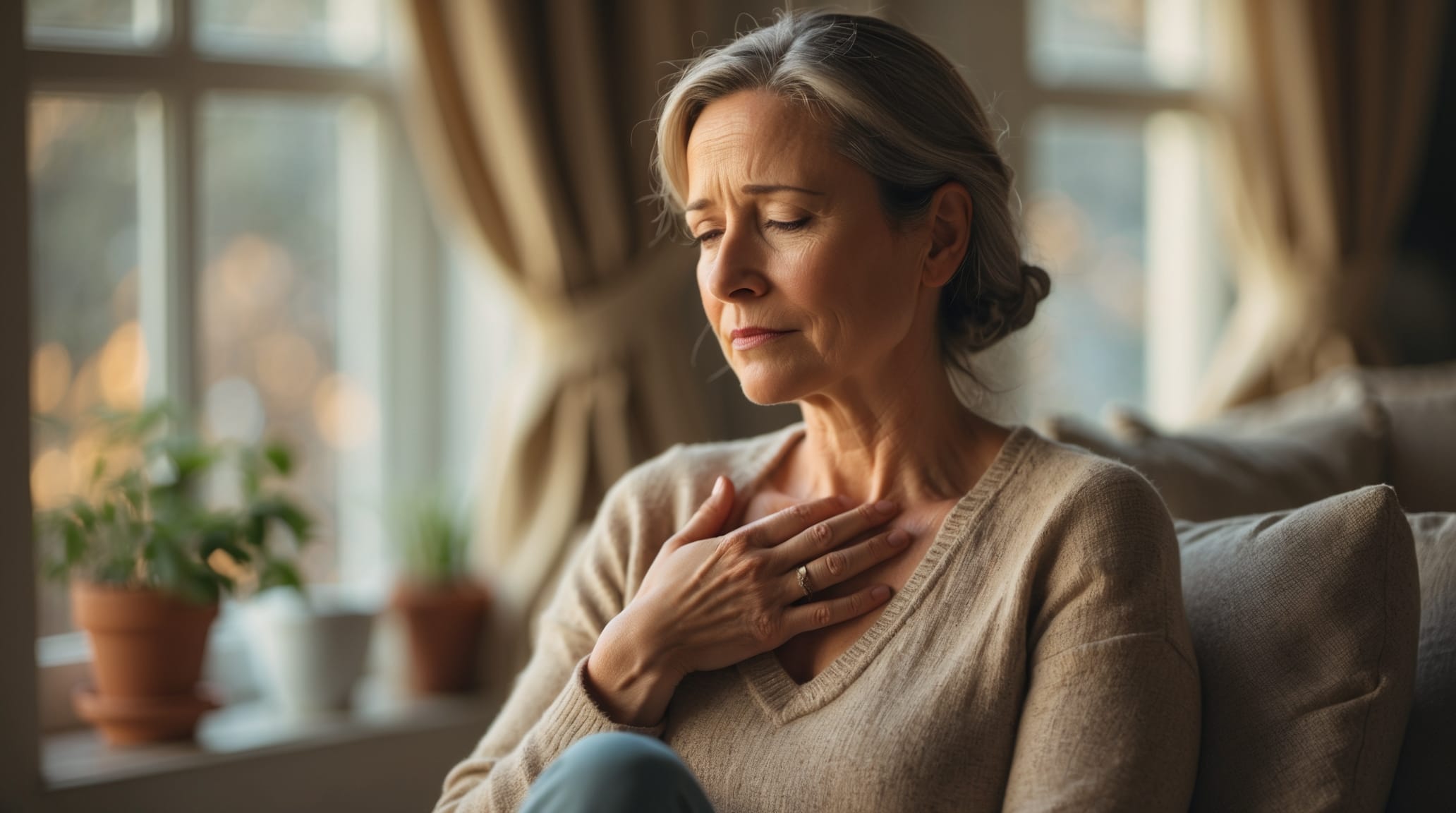

Picture this: It’s 2 AM before a big presentation. Your mind is racing—and your body is, too. Tight chest, churning stomach, sore muscles. Tests come back “normal,” but you don’t feel normal.
Here’s the bridge: anxiety can signal your immune system to release pro-inflammatory molecules that influence pain sensitivity, gut function, heart rhythm, and more. That’s psychoneuroimmunology in action.
What Your Body Is Actually Doing
During anxiety, brain regions involved in threat detection modulate autonomic output and immune signaling. Circulating cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α can rise and interact with neural circuits that regulate mood and interoception.
The Anxiety ↔ Inflammation Cycle
1) Perceived threat → 2) Brain–immune signaling → 3) Cytokine release → 4) Physical symptoms → 5) More anxiety → 6) Continued inflammation.
7 Ways Anxiety Can Amplify Physical Symptoms
1) Heart & Chest Sensations
Stress can transiently affect vascular tone, autonomic balance, and inflammatory signaling—producing tightness, fluttering, or pressure despite normal cardiac tests.
2) Gut–Brain Highway
The vagus nerve and inflammatory mediators shape motility, barrier integrity, and visceral sensation—explaining nausea, cramping, and urgency during acute worry.
3) Muscle & Fascia Tension
Sympathetic arousal + cytokines can heighten nociception and stiffness, creating “flu-ish” aches or heavy limbs when stress runs high.
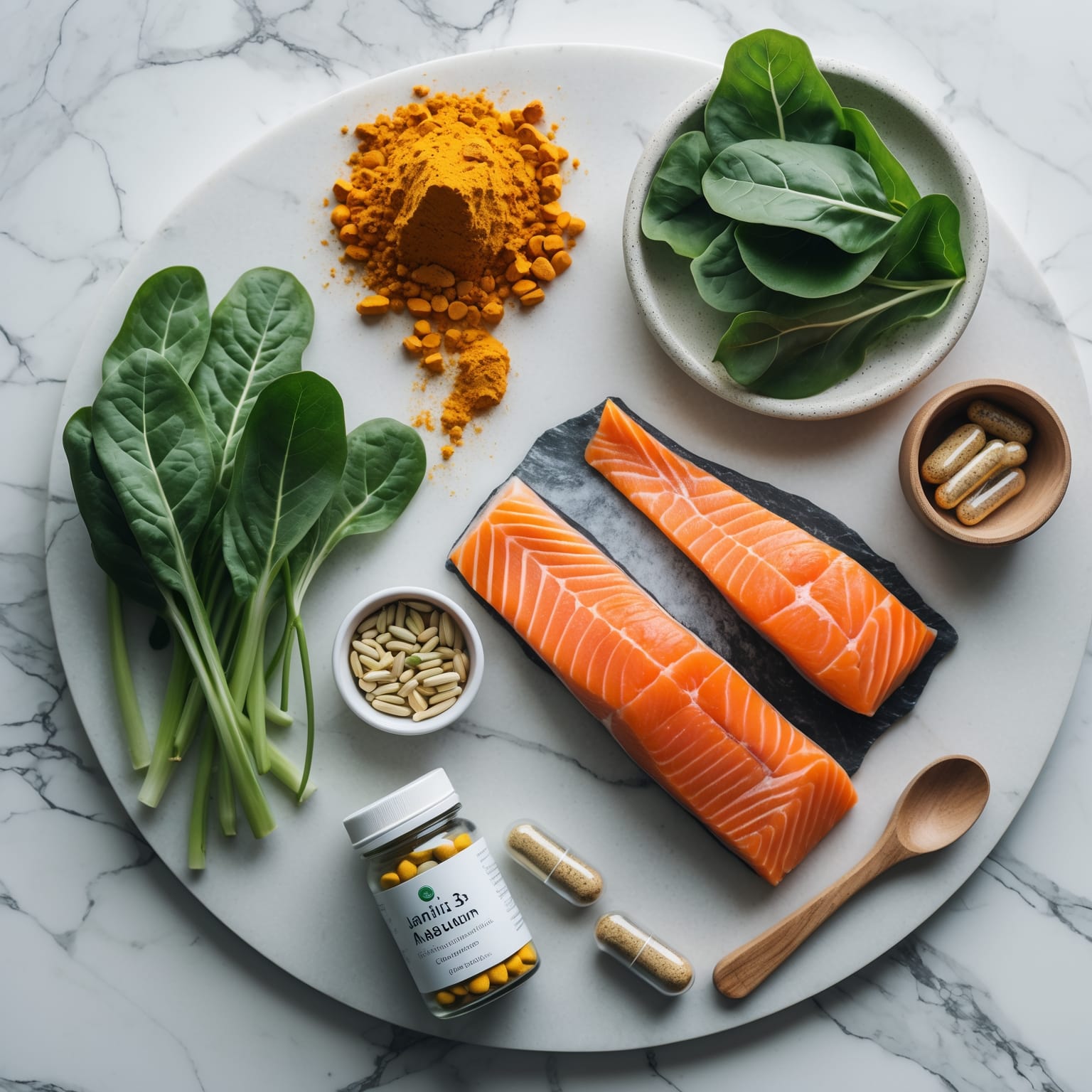

Breaking the Cycle: Evidence-Informed Strategies
Strategy 1: Target Systemic Inflammation
Omega-3s (EPA/DHA): In an RCT, omega-3 reduced anxiety and lowered IL-6/TNF-α production vs. placebo. Kiecolt-Glaser et al., 2011. :contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}
Dietary pattern: Emphasize omega-3 fish, extra-virgin olive oil, colorful plants, legumes, fermented foods; reduce ultra-processed/sugary foods that promote low-grade inflammation.
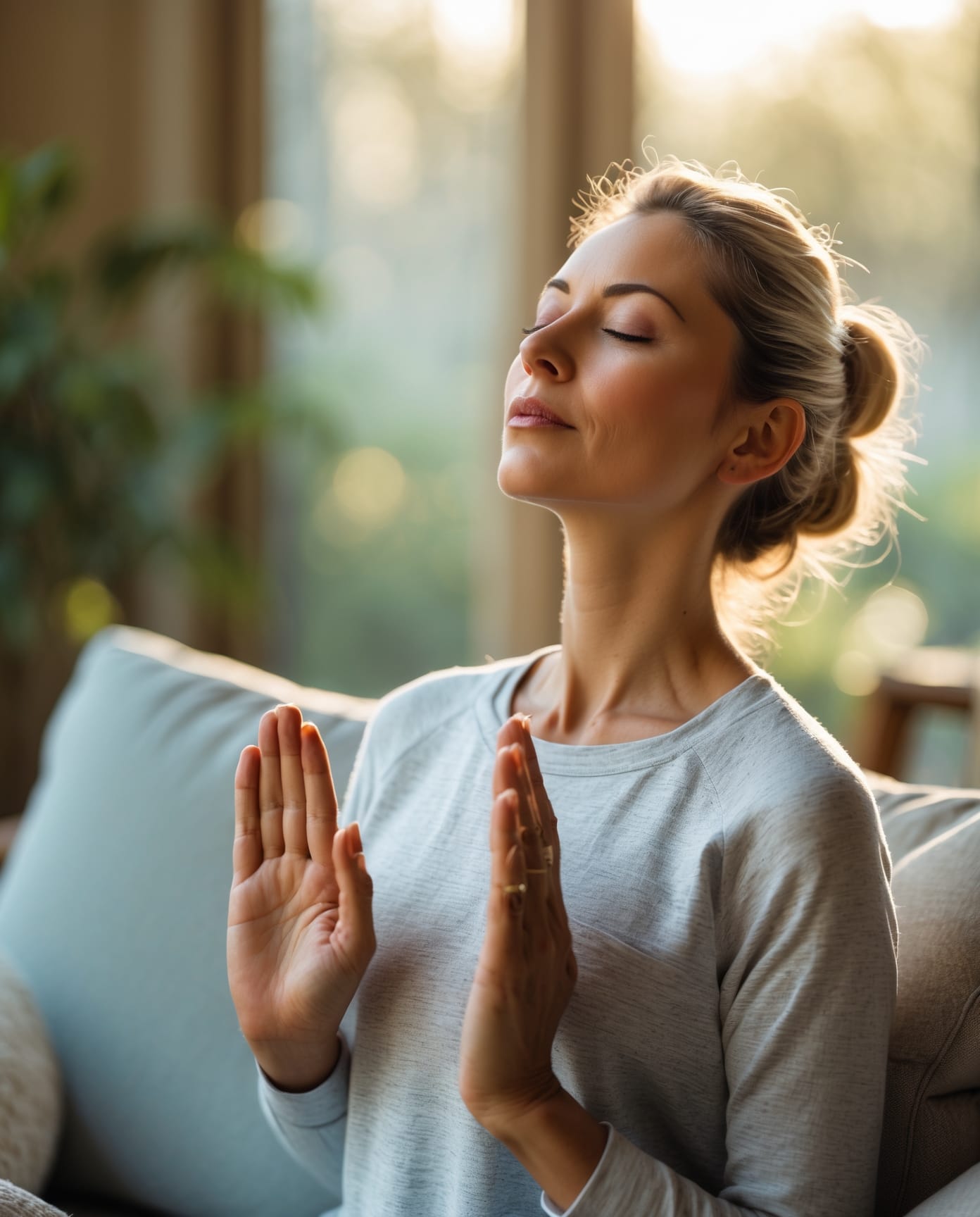
Strategy 2: Engage the Anti-Inflammatory Reflex
Breathwork & vagal tone: Slow-paced breathing (e.g., 4-7-8) can acutely shift HRV and support autonomic balance; theoretical and empirical work suggests vagal pathways are a mechanism. See Gerritsen & Band, 2018 (model) and Vierra et al., 2022 (physiologic shifts). :contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}

Strategy 3: Midlife Hormone Context
Perimenopausal estrogen decline is associated with a more pro-inflammatory milieu, which can sensitize stress responses. See mechanistic and clinical reviews: Zhang et al., 2024; Russell et al., 2019. :contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
Ready to address both anxiety and body symptoms?
Get a tailored plan that blends nervous-system regulation with low-inflammation routines.
Meet Mara, Your Anxiety Navigation CoachWhen to Seek Medical Care
- Chest pain with radiation to arm/neck/jaw
- Severe breathing difficulty or throat tightness
- Sudden, worst-ever headache
- Palpitations with dizziness, syncope, or neurologic symptoms
Your Symptoms Are Valid—and Modifiable
The psychoneuroimmunology frame validates why anxiety can feel physical—and gives you multiple levers (breath, sleep, nutrition, pacing, therapy) to dial it down.
FAQ
Autonomic shifts are near-instant; inflammatory changes can follow within minutes to hours depending on context and baseline inflammation.
Not always. Systemic markers (e.g., CRP) may be normal even when local or transient immune signaling contributes to symptoms.
Often yes. In RCTs, omega-3 reduced both inflammatory output and anxiety scores; paced breathing improves HRV and calm states. :contentReference[oaicite:5]{index=5}
Key citations used on this page: Costello 2019 (BMJ Open); Kiecolt-Glaser 2011 (Brain Behav Immun); Gerritsen & Band 2018; Vierra 2022; Zhang 2024; Sara 2022.
Related Articles
Why Your Anxiety Feels So Much Worse After 40
Hidden brain and hormone shifts that amplify anxiety in midlife—and how to adapt.
How Poor Sleep Amplifies Anxiety and Shame
Understand the loop and break it with small, steady levers.
Why Shame Makes Your Body Hurt
When emotions sensitize the body—and ways to soothe.